Natural and Anthropogenic Ground Movements
The mapping of potential hazards such as reactive soil movements, subsidence, landslides and earthquakes due to natural and anthropogenic ground movement is the focus of this project. This project is closely related to my previously discussed projects and aims to monitor and manage geohazards for more resilient communities.
Different methods will be used in the investigations including
- Interfereometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR)
- Hydro-mechanical finite elemnt modelling (FEM)
- Deep Learning (DL)
- Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
One of the investigations analysed the Western Melbourne area that is prone to significant ground movement due to reactive soils shown below. 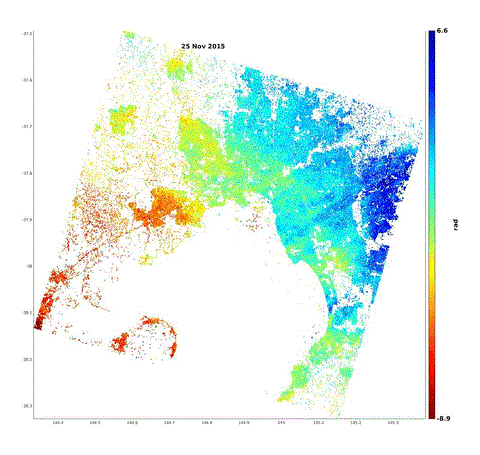
Publications:
- Gedara, S.D.D.A., Wasantha, P.L.P., Teodosio, B. and Li, J., 2021. An Experimental Study of the Size Effect on Core Shrinkage Behaviour of Reactive Soils. Transportation Geotechnics, p.100709. (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2021.100709)
- Teodosio, B., Baduge, K.S.K. and Mendis, P., 2020. Simulating reactive soil and substructure interaction using a simplified hydro-mechanical finite element model dependent on soil saturation, suction and moisture-swelling relationship. Computers and Geotechnics, 119, p.103359. (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.103359)
- Teodosio, B., Baduge, K.S.K. and Mendis, P., 2020. Relationship between reactive soil movement and footing deflection: A coupled hydro-mechanical finite element modelling perspective. Computers and Geotechnics, 126, p.103720. (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103720)
